Motion of Planets and Satellites
Motion of Planets and Satellites: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as Motion of Satellites, Orbital Speed of Satellites, Orbital Time Period of Satellites, Gravitational Potential Energy of Satellites, Kinetic Energy of Satellites, Conservation of Total Energy in Satellites, etc.
Important Questions on Motion of Planets and Satellites
Satellites are orbiting around the earth in orbits of ratio , respectively. The ratio of their areal velocities is
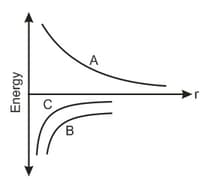
The figure shows the variation of energy with the orbit radius of a body in circular planetary motion. Find the correct statement about the curves A, B and C
A satellite revolves in the geostationary orbit but in a direction east to west. The time interval between its successive passing about a point on the equator is
A satellite is launched into a circular orbit above the surface of the earth. Find the period of revolution in nearest integer (in hours) if the radius of the earth is and the acceleration due to gravity is (Take and ).
Which of the following statement is always true for a binary star system?
A satellite is revolving in a circular orbit at a height from the earth's surface (radius of earth ; ). The minimum increase in its orbital velocity required, so that the satellite could escape from the earth's gravitational field, is close to (Neglect the effect of atmosphere.)
A synchronous satellite goes around the earth once in every What is the radius of orbit of the synchronous satellite in terms of the earth's radius?
(Given: mass of the earth, , radius of the earth, and universal gravitational constant, )
If due to air drag, the orbital radius of the earth decreases from to , then the expression for increase in the orbital velocity is:
At perihelion, the mechanical energy of Pluto's orbit has:
A satellite close to the earth is in orbit above the equator with a period of revolution of hours. If it is above a point on the equator at some time, it will be above again after time
Suppose the gravitational force varies inversely as the power of the distance. If a satellite describes a circular orbit of radius under the influence of this force, then the time period of the orbit is proportional to
The time period of a satellite of earth is . If the separation between the earth and the satellite is increased to times the previous value, the new time period will become.
The moon revolves round the earth times in one year. If the ratio of sun-earth distance to earth-moon distance is , then the ratio of masses of sun and earth will be
If the universal constant of gravitation were decreasing uniformly with time, then a satellite in orbit would still maintain its
A body revolved around the sun times faster than the earth. What is the ratio of their radii?
The earth revolves round the sun in one year. If the distance between them becomes double, the new period of revolution will be-
If mass of a satellite is doubled and time period remain constant the ratio of orbit in the two cases will be-
The orbital speed of a satellite revolving nearby the earth is:
A geostationary satellite orbits around the earth in a circular orbit of radius . Then, the time period of a spy satellite orbiting a few hundred kilometres above the earth's surface will approximately be :
